- Causes of the problem
- What is the rate of hair loss per day?
- Hair life cycle
- Telogenous alopecia, a temporary, reversible form
- Hair loss prevention
- Prevention principles
- Types of hair loss
- Possible Causes of Hair Loss
- Diseases that lead to excess hair loss
- Which doctor should i contact for excess hair loss
- Diagnostics and examinations for excess hair loss
- What to do with increased hair loss
- METHODS FOR TREATMENT OF Alopecia with CLIMAX
- - Medication methods
- - Lifestyle changes
- - Folk remedies
- HOW TO DIFFER ANDROGEN-DEPENDENT HALOPECIA FROM OTHER TYPES OF HAIR LOSS
- FOCAL ALOPETIA
- Hair loss treatment after 50
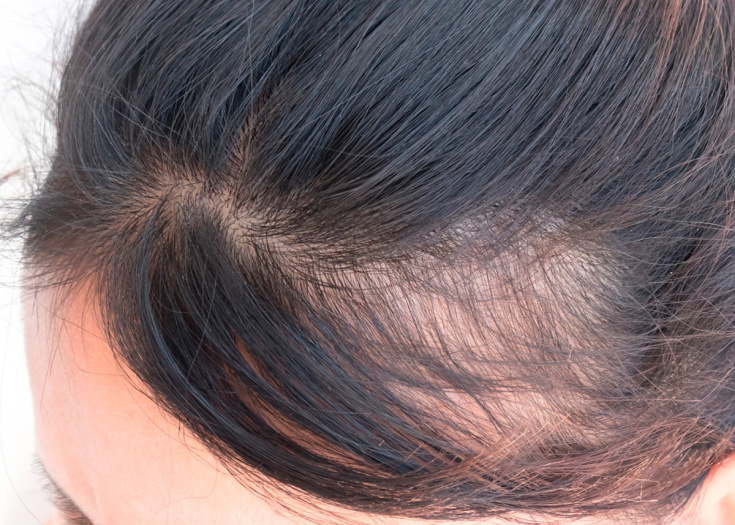
Age, close to 50 years, 🧓🏻 is not easy for the fair sex. 🛑 Physiological processes adversely affect the appearance. 👵🏻 Perhaps the main concern is increased hair loss after 50 years.
Causes of the problem
Throughout life, and elegant age is no exception, ladies have to resist many factors harmful to hair:
- emotional, psychological stress;
- unbalanced diet;
- physical overload;
- unfavorable climate;
- trichological, dermatological diseases;
- endocrine disorders;
- acute infections;
- blood loss;
- some types of therapy;
- traumatic perms, combing, hot drying;
- unsuitable cosmetics.
These factors are very important, however, the priority causes of hair loss in women over 50 follow from hormonal processes in the body.
During menopause, the hormonal background is unstable. With the onset of menopause, the percentage changes towards a decrease in the proportion of female hormones and an increase in male hormones.
The main male hormone, testosterone, causes active degeneration of hair follicles. Thinning and fragility of hair shafts, weakening of the bulbs, excess of the loss rate are characteristic signs of a deficiency of the main female hormone - estrogen.
What is the rate of hair loss per day?
On average, between 100,000 and 150,000 hairs grow on our scalp, and the rate of hair loss is 50-100 hairs every day. This happens because the hair on the head is constantly being renewed.
Hair life cycle
- growth phase (anagen)
- growth retardation phase (catagen)
- resting phase (telogen)
- phase of shedding and the interval between the emptying of the follicle and the growth of new hair (exogenous)
This daily shedding is a natural biological process in men and women.
Daily hair loss does not lead to a decrease in the total mass of hair, since the growth cycles are asynchronous - all hairs are in different phases. The independent growth cycle of each follicle prevents sudden, one-time hair loss.
However, in some cases, hair loss increases and becomes more excessive.
This process may be due to:
- Irregularities in the hair growth cycle
- Microinflammation
- Damaging hair follicles
- Hereditary or acquired diseases
- Various external and internal factors
Each of the factors can become a "trigger" for loss.
Telogenous alopecia, a temporary, reversible form
This is a common type, but it is quite intense in its clinical manifestations of hair loss. It is characterized by an abrupt loss of a large amount of hair due to the premature transition of hair to the telogen phase.
Telogenic alopecia differs in the form of its course
- Sharp Telogenous alopecia can occur at any age and is equally common in men and women. The duration of acute telogenous alopecia is less than 6 months.
- Chronic telogen alopecia is observed mainly in women aged 30 to 60 years, who do not have other diseases. And it can last over 6 months.
Hair loss prevention
The hair follicle is a dynamic structure that is very sensitive to external changes. The rate at which each cycle of the hair follicle proceeds depends largely on various factors such as hormones, nutrients, toxins, and biologically active molecules. Hair loss is most often associated with irregularities in their life cycle. These disorders can be caused by external or genetic mechanisms. It should be understood that there is no prophylaxis for hereditary baldness (androgenetic alopecia).
Extrinsic prolapse can be prevented with significantly less effort than the treatment itself. Most people start thinking about preventing hair loss only after losing a large amount of hair.
Prevention principles
A balanced diet and a healthy lifestyle. The first and basic principle is to maintain overall health and maintain a healthy lifestyle. Skin, hair and nails are indicators of the general condition of the body. Hair loss can often be one of the first signs of internal pathology or insufficient intake of substances.
Annual medical examination will allow assessing the state of general health, and an adequate diet will ensure a full intake of substances involved in the construction of hair follicle structures in the body, which will prevent possible baldness.
Hair is made up of protein, so adequate protein intake is required for proper growth. Iron, calcium, zinc and vitamin B will help both keep hair from falling out and maintain a normal growth cycle, and lack of them can lead to massive hair loss. Dramatic weight loss with a weight loss of more than 20 kg and an unbalanced diet can have a shock effect on the dividing cells of the follicles and, as a result, negatively affect the balance of hair growth and loss.
For the maturation and normal functioning of hair follicle cells, a large amount of iron is required. The problem of latent iron deficiency remains relevant among the adult population due to the lack of balance in iron intake. In addition, women experience a monthly loss of this trace element during menstruation. Obesity is also a risk factor for the development of iron deficiency.
It is important to understand that iron saturation may be sufficient for erythropoiesis and hemoglobin synthesis, but already low for many biological processes.
A monotonous diet with no animal products, low calorie intake, malabsorption diseases of the gastrointestinal tract can lead to iron deficiency and, as a result, hair loss up to baldness. Eating well and being a nutritionist remains commonplace, but key to preventing hair loss.
Proper scalp hygiene. An equally important principle is proper scalp care. Excess sebum in the scalp area promotes the multiplication of yeasts, which break down it into fatty acids, which irritate the scalp.
The inflammatory process can contribute to hair loss, so timely hygiene to flush out excess sebum is an important preventive measure to maintain a healthy scalp area.
One may come across the opinion that frequent shampooing causes hair loss in persons with a predisposition to baldness.This is not true. The scalp, like any part of the skin, requires careful hygiene. Each hair has a large sebaceous gland, so a large amount of sebum (sebum) is secreted in this area every day. Hair falling out during washing is in fact already dead, non-growing structures that would fall out regardless of this.
The use of balms and conditioners for the hair shaft is very important in balancing the negative charge of the shampoo and maintaining the healthy structure of the hair follicle.
Consideration of related factors. The third principle is obvious, but nevertheless often overlooked by patients. Factors that have a damaging effect on the hair should be avoided. Excessive pulling of hair into a ponytail or bun can disrupt their growth with prolonged wearing of such a hairstyle. Any chemical agents have a damaging effect on the hair structure.
Brushing and rough rubbing with a towel injures damp hair and can cause some of the growing hair to fall out and break off. Using a hair dryer also damages the follicles, as it dries out the skin and its structures in addition to the hair. Alternating with natural drying will limit this negative factor.
Types of hair loss
- Androgenic or androgenetic alopecia is the most common form of hair loss, affecting up to 80% of men and 50% of women.
- Diffuse alopecia is more common in women.
- Psychosomatic or nervous alopecia.
- Alopecia areata, which is currently considered an autoimmune process.
- Cicatricial, or infectious alopecia.
- Age-related alopecia.
- Seasonal alopecia.
Possible Causes of Hair Loss
Pathology of hair growth (partial loss, total baldness, hirsutism, hypertrichosis) occurs due to disturbances in the course of the hair cycle. The most common cases of hair loss are the premature end of the anagen phase and the early onset of the catagen phase.
- During puberty, when hormonal changes in the body occur, there is an increased production of sebum and excess hair loss. At the end of puberty, the processes of most people return to normal.
- The capillaries of the hair papilla in males, genetically predisposed to baldness, have an increased sensitivity to male sex hormones. With an increase in the content of androgens during puberty, persistent vasospasm of the papillae of the scalp occurs and, as a result, hair loss. On the contrary, in other parts of the body, including the face, such men experience abundant hair growth, which is also explained by the action of androgens.
- Despite the increased secretion of estrogen during pregnancy, many women complain of excess hair loss, especially in the 2nd and 3rd trimesters. This is due to the fact that at this time almost all nutrients entering the woman's body are spent on the growth of the fetus. Postpartum hair loss is due to the increase in the number of hairs in the telogen phase.
- Usually, the restoration of hair growth cycles in a woman occurs 4-6 months after the birth of the child.
- Increased hair loss can be stressful. In patients with disturbed periods of sleep and wakefulness, decreased memory, with obsessive states, various changes in the biopotentials of the brain are observed, which can lead to a violation of the trophism of the hair follicle.
- Exogenous factors (insolation, dry air, the use of a hot hair dryer, aggressive shampoos, paints) have a negative effect on the condition of the hair. This occurs due to the violation of the "tile-like" arrangement of hair scales, leading to splitting of the hair shaft and increasing its fragility.
Taking certain medications (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, anticoagulants, thyreostatics, antidepressants, cytostatics, beta-blockers, interferon alpha drugs, anticonvulsants, antiparkinsonian, anthelmintic, antiherpetic, antiviral, antibacterial drugs, and oral contraceptives). lead to increased hair loss.
In 80% of cancer patients taking cytostatic drugs, hair loss occurs 10 days after the start of treatment.
Infectious, autoimmune, systemic diseases, endocrine pathologies also affect excess hair loss.
As a person ages, scalp hair growth may be stable, but the anagen phase tends to shrink. Hair becomes thinner and more brittle. Hair loss is more common in women over 50 and diffuse in nature.
Diseases that lead to excess hair loss
- Diseases of the thyroid gland, hypothalamic-pituitary system, ovaries, adrenal glands, etc.
- Autoimmune diseases (nodular goiter, idiopathic hypoparathyroidism, Hashimoto's thyroiditis).
- Dermatological diseases (seborrhea, psoriasis, eczema, etc.).
- Diseases of internal organs and systems (gastritis, colitis, kidney and liver diseases).
- Avitaminosis.
- Chronic infections (tonsillitis, sinusitis, sinusitis).
- Cytomegalovirus infection.
- Syphilis.
- Tuberculosis.
- Immunodeficiency states.
Which doctor should i contact for excess hair loss
In case of increased hair loss, you should consult a dermatologist or trichologist. In the future, it may be recommended to consult an endocrinologist, therapist, gastroenterologist, neurologist, gynecologist, phthisiatrician, rheumatologist.
Diagnostics and examinations for excess hair loss
To find out the cause of hair loss, the doctor may prescribe a set of laboratory and instrumental survey methods:
- clinical blood test to determine the concentration of hemoglobin, the number of erythrocytes, leukocytes and platelets, hematocrit and erythrocyte indices (MCV, RDW, MCH, MCHC), leukoformula and ESR (with microscopy of a blood smear in the presence of pathological changes);
- general urine analysis;
- C-reactive protein (CRP);
- biochemical blood test, including: total protein, albumin, protein fractions; assessment of renal performance (urea, creatinine, glomerular filtration); assessment of liver performance indicators (bilirubin, ALT, AST).
If you suspect pathological processes in the thyroid gland, appoint:
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland, parathyroid glands and regional lymph nodes;
- Total triiodothyronine (total T3);
- Free triiodothyronine (free T3);
- General thyroxine (total T4);
- Free thyroxine (free T4);
- Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH);
- Antibodies to thyroglobulin (AT-TG);
- Antibodies to thyroid peroxidase (AT-TPO).
Diagnosis of deficiency states includes:
- diagnostics of anemias;
- erythropoietin;
- transferrin;
- latent (unsaturated) iron-binding capacity of blood serum;
- serum iron;
- folic acid;
- vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamin);
- phosphorus, nails;
- zinc, serum;
- copper, serum;
- chrome, hair;
- silicon, hair.
What to do with increased hair loss
To determine the cause of increased hair loss, you need to see a doctor. After consulting with a specialist, the patient should follow his recommendations and prescriptions.
For the duration of treatment, you should abandon hair dyeing, perm and tight hairstyles.
A balanced diet, restriction of caffeine, which causes vasospasm, and the obligatory wearing of a headgear in the cold season can improve the prognosis of treatment.
METHODS FOR TREATMENT OF Alopecia with CLIMAX
Do not wait for the bald patches on your head to become visible not only to you, but also to those around you.There are several effective methods, some of which will slow down hair loss and some will help restore your hair style.
- Medication methods
The doctor can prescribe a drug that contains the correct dose of estrogen, and thus solve the problem of baldness. You can also use sprays with minoxidil, which have a direct effect on the root of the hair, accelerate blood circulation and stimulate new hair growth.
- Lifestyle changes
One of the causes of excess androgen production is low sleep, lack of exercise and poor diet. By normalizing these areas, you will heal your body and prevent hair loss.
- Folk remedies
Considering the original hair type and your financial capabilities, select several useful recipes based on traditional medicine. These masks will be of great help in your fight against alopecia.
In addition, you need to take care of your hair with professional balms and shampoos. If the fact of the formation of a receding hairline has already occurred, you can always turn to the seamless HFE operation. This is an innovative hair transplantation technique that does not leave scars and allows you to restore the lost hair.
HOW TO DIFFER ANDROGEN-DEPENDENT HALOPECIA FROM OTHER TYPES OF HAIR LOSS
Androgen-dependent alopecia can start imperceptibly: there will be no sudden hair loss. The patient will feel that greasiness increases, the fronto-parietal zone begins to lose volume, the hair becomes thinner, thinning over time. The occipital zone (androgen-independent) remains unchanged. In women, at the onset of the disease, the whiskey may become thinner. In men, this phenomenon was not observed.
The disease can occur locally, only gradual hair loss will become a visible problem. But there are times when there are gynecological pathologies (polycystic ovaries), acne.
Since the cause of androgen-dependent alopecia is directly related to the woman's hormones, self-medication should never be done here. Irreparable damage to health can be caused. At the first signs of the disease, urgently consult a specialist.
FOCAL ALOPETIA
Alopecia areata or alopecia areata is a disease in which hair falls out in patches. The number and size of the lesions can be any and be localized anywhere: on the head, on the eyebrows, eyelashes, in the armpits. The cause of the development of alopecia areata is an autoimmune process. Simply put, the immune system mistakenly attacks its own body, hair follicles.
In 2012, American scientists identified eight genes that influence the development of focal alopecia. Researchers have also found ULBP3 proteins in the hair follicles of people with alopecia areata, which should not normally be present. Cells marked with these proteins are destroyed by the immune system, which leads to hair loss.
The exacerbation of foci of chronic infection, parasitic infestations, viral infections, trauma, stress, and the intake of certain medications provoke an exacerbation. Alopecia areata can occur at any age, often combined with other autoimmune diseases: atopic dermatitis, hay fever, bronchial asthma.
Hair follicles remain alive, growth may resume, but there are types of alopecia areata in which the prognosis is unfavorable:
- Subtotal form - more than 40% of hair is missing on the scalp;
- Ophiasis - baldness along the marginal zone of hair growth - the back of the head, forehead, temples;
- Total form - complete absence of hair on the head;
- Universal shape - there is no hair on the head, in the area of eyebrows, eyelashes, on the skin of the trunk and limbs, there is a complete or partial loss of hair.
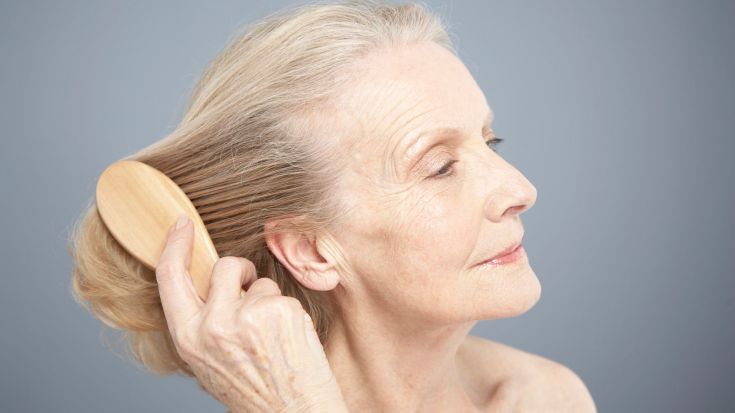
Hair loss treatment after 50
Effective treatment for hair loss in women over 50 should be comprehensive.
Currently, hormone replacement therapy is successfully used to prevent sudden age-related changes in appearance and well-being.It is necessary for every woman to consult a gynecologist-endocrinologist, even in the absence of characteristic symptoms.
The trichologist is a reliable assistant for ladies who want to keep their lush hairstyle until old age.
A course of trichological procedures allows to stop losses, restore a healthy hairline. The doctor selects drugs, cosmetic products, the intensity of the course individually for each patient.
At the same time, there is a set of the most effective procedures suitable for almost all healthy women:
- microinjection of stimulating drugs (mesotherapy);
- manual, as well as cryomassages of the hairy zone;
- electrical stimulation;
- reflexology;
- spa treatments;
- plasma lifting;
- laser therapy;
- vitaminization.
Hair loss in women in their 50s is usually successfully corrected. The main thing is to contact the clinic in a timely manner.