- CAUSE OF HAIR LOSS IN WOMEN AFTER 30 YEARS OLD # 1: HORMONAL DISORDERS
- TREATMENT METHODS
- CAUSE OF WOMEN'S HAIR LOSS # 2: STRESS
- TREATMENT METHODS
- CAUSE OF HAIR LOSS AFTER 30 YEARS OLD # 3: LACK OF VITAMINS AND MICROELEMENTS
- TREATMENT METHODS
- CAUSE OF EXTRAORDINARY HAIR LOSS IN WOMEN # 4: INCORRECT HAIR CARE
- TREATMENT METHODS
- CAUSE OF HAIR LOSS AFTER 30 YEARS # 5: HEREDITARY
- TREATMENT METHODS
- Common Causes of Hair Thickness Loss
- Other causes of hair loss in girls
- Hair loss symptoms
- Classification and developmental stages of hair loss
- Hair Loss Treatment
- Drug treatment
- Surgery
- Physiotherapy treatment
- Conclusion
Hair loss after the age of 30 👩🦱 usually causes panic in women and a desire to urgently solve the problem. 😨 The most obvious for most of the fairer sex 💃🏻 is the use of cosmetics that promise to return the former thickness of hair. 👸🏻 However, only in rare cases is it possible to achieve the cherished goal only through the use of shampoos, oils and masks.
The fact is that problems usually lie within the body. This means that the first and only correct step towards hair restoration is a visit to a doctor and a diagnosis.
CAUSE OF HAIR LOSS IN WOMEN AFTER 30 YEARS OLD # 1: HORMONAL DISORDERS
The thyroid gland is an organ that is sensitive to stress, medication, diet, and simply unhealthy diet. If it starts to malfunction, it instantly affects the hair. So, in the case of an excess of hormones, the stiffness of the hair increases, and they begin to evenly fall out over the entire head. With a lack of hormones, the hair becomes thin and dull, falling out both from the head and from the whole body.
Another hormonal cause is the premenopausal period, when estrogen production decreases and testosterone levels can rise. Then hair begins to fall out on the head and grow - on the chin and above the upper lip.
You should consult an endocrinologist for hair loss if you notice:
- changes in hair structure, thinning and weakness;
- loss of eyebrows along the outer edge;
- hair loss on the head and body;
- coarseness and stiffness of the hair;
- discoloration of hair;
- change in waviness - straight lines begin to curl, and wavy ones begin to straighten.
Your doctor will prescribe tests for you and determine which hormone therapy to prescribe.
TREATMENT METHODS
First of all, it is necessary to exclude the intake of alcohol and smoking, which negatively affect the work of the endocrine system and can affect the test results. In young women, thyroid problems are usually expressed in its hyperfunction. In this case, "anti-thyroid" drugs, radioactive iodine are prescribed, and sometimes there may be a question about surgical removal of the thyroid gland.
Shown is a dairy-plant diet. For older women, an endocrinologist will most likely prescribe replacement therapy, which will make up for the deficiency of female sex hormones or thyroid hormones.
In all cases associated with disorders of the endocrine system, treatment should be carried out under the constant supervision of a physician, since the doses of drugs are prescribed purely individually and should be regulated depending on the results of a blood test. In addition, taking thyroid-enhancing drugs may require prescribing cardiovascular drugs to regulate blood pressure. Self-medication is categorically unacceptable.
CAUSE OF WOMEN'S HAIR LOSS # 2: STRESS
Stress is almost a natural environment for a modern woman.Strenuous work, family responsibilities, household chores, driving a car - all this leads to sleep disturbances, neurotic conditions and deterioration in the quality of hair and skin. The fact is that during stress in the body, B vitamins, which are so necessary for hair, are consumed at a tremendous rate. Therefore, the latter can fall out, as they say, on the basis of nerves.
TREATMENT METHODS
The main thing in this case is to restore mental balance, to follow the mode of work and rest, diet, to walk and move more. This will immediately improve the appearance of your hair and skin. If you feel that stress is becoming chronic, and a little rest or even a trip on vacation does not help, you should seek help from a neurologist.
He will probably prescribe medications for you that will help improve sleep, relieve tension, and restore the normal functioning of the nervous system. Anti-stress vitamin and mineral complexes, spa treatment, physiotherapy, swimming will also be useful.
CAUSE OF HAIR LOSS AFTER 30 YEARS OLD # 3: LACK OF VITAMINS AND MICROELEMENTS
For whatever reason hair falls out, it has been proven that in 90% of women this problem is accompanied by iron deficiency and a lack of the amino acid lysine. Therefore, the diet must necessarily contain meat, fish and eggs, or you should take care of taking special food supplements. A nutritionist will help you with this.
TREATMENT METHODS
Pay attention to your exercise regimen. You may be overworking your fitness routine, driving your body into a stressful regime. In no case should you "sit down" on rigid diets completely devoid of fats, this has a detrimental effect not only on the condition of the hair, skin and nails, but also on the nervous system. Opt for oily fish and olive oil for the benefit of your hair.
A nutritionist will advise you on vitamin-mineral complexes and dietary supplements containing in sufficient quantities the so-called fat-soluble vitamins A, E, D, "neurovitamins" of group B, and will make an individual program of proper nutrition.
CAUSE OF EXTRAORDINARY HAIR LOSS IN WOMEN # 4: INCORRECT HAIR CARE
Of course, a perfectly healthy young woman can start to lose hair. Most likely, they do not even fall out, but break off at the roots. This is usually due to improper care. It can also be caused by frequent dyeing, perm, hair extensions, or specific hairstyles such as braids or dreadlocks. The trichologist will be able to tell you exactly how and how your hair is damaged and will prescribe remedies for caring for them.
In this situation, it is important not to be led by fashion and not to try the advertised miraculous remedies on yourself without the appointment of your trichologist, otherwise you can only aggravate the situation.
TREATMENT METHODS
Stop all procedures that are traumatic for hair: coloring, curling, complex styling. Give your hair a rest. Pay attention to the quality of the water you wash your hair with. If the water is too hard, it can be softened by boiling or using a water filter. It is better to choose shampoos that are pH-neutral, natural and silicone-free.
The trichologist can prescribe special oils, masks and serums, as well as a course of mesotherapy to improve hair growth. To reduce the weight of the hair and the stress on the hair roots, it may be necessary to shorten the haircut.
CAUSE OF HAIR LOSS AFTER 30 YEARS # 5: HEREDITARY
What to do if hair loss in a woman after 30 is due to purely genetic reasons? Here it remains only to take note of your characteristics and think about how to make thinning hair thicker. Some people prefer wigs, someone chooses the extension of artificial strands, others come up with extreme options for shaving the head bald.However, these are all temporary and not always convenient options, often harming the scalp and hair follicles.
TREATMENT METHODS
In the case of hereditary alopecia, hair transplantation can be recommended. All methods are based on the fact that, as a rule, viable hair follicles (“bulbs”) remain in the occiput region, which can be transplanted into problem areas. There are only three transplantation methods. The oldest and most traditional is the patchwork method, when a strip of skin is taken from the back of the head, excised into small pieces with hair follicles, and then they are implanted into incisions prepared in advance with a scalpel in the balding area.
After that, a scar inevitably remains on the back of the head, as in the recipient zone. Therefore, today this method is practically not used. The other two most popular methods are FUE Machine and FUE Hand (including the HFE method). They are less traumatic than the flap method, due to the removal of the smallest fragments of skin with follicles from the donor area, which can be implanted immediately.
In the first case, the donor material is taken with a special machine, in the second - practically by hand, but also with the help of special instruments. The "manual" method is more suitable for women, as it is the most gentle, accurate and painless. With its help, about 6,000 hair follicles can be transplanted in one procedure under local anesthesia, after which neither scars nor pronounced edema remains. A woman can leave the clinic in a few hours as if nothing had happened and return to everyday life, just with thicker hair.
If it is necessary to further increase the density of the hair, the procedure can be repeated after a year.
Common Causes of Hair Thickness Loss
Common causes of scalp hair loss in girls include:
- Stress. Constant arguments with parents or with peers, problems with classmates, a young man, a break in relations - all these factors negatively affect not only the psychological state of the girl, but also cause hair loss. And this happens because during stress, the narrowing of the capillaries is observed, as a result of which the blood supply in the hair follicles is disrupted, and the hair begins to crumble.
- Weakened immunity. When the body is depleted, this is immediately manifested by thinning of the nail plate, deterioration of the skin condition, as well as hair loss.
- Negative environmental impact. An increased level of radiation, air polluted with waste and harmful elements, a violation of the temperature regime (walking on the street in winter without a hat or in summer without a hat) - these factors can cause hair loss.
- Heredity. If mom, grandmother or great-grandmother could not boast of beautiful thick hair, it was brittle and dry, then the daughter / granddaughter's hair will be prone to falling out.
- Serious medical problems (for example, diabetes, thyroid disease, etc.).
Other causes of hair loss in girls
The cause of severe hair loss in girls can also be:
- Reorganization of the body. Adolescence is a time when young girls experience hormonal changes. And if at this moment some disturbances occur, for example, the amount of the male hormone in the body rises, then this can lead to hair loss.
- Passion for diets. Many girls, in the fight for a beautiful figure, risk losing their beautiful curls. With a sharp decrease in weight, the amount of adipose tissue in the body decreases, hormonal levels change, which leads to hair loss.
- Pregnancy and childbirth. In girls who are in an interesting position, the hormonal background changes, the body's defenses weaken, as a result of which the process of hair loss intensifies.
- Cancellation of contraceptive drugs. Before deciding on such a method of contraception as birth control pills, you need to understand that they lead to a change in hormonal levels, which can adversely affect the health of the hair.
- Negative mechanical effect on hair, improper hair care. Washing the head with shampoos, which contain aggressive substances, frequent hair drying with a hairdryer, "chemistry", paint abuse, build-up, excessive discoloration, and so on - all this leads to thinning hair.
- Dermatological problems. Diseases such as seborrhea and psoriasis dramatically increase the amount of hair loss. Due to an excess of sebum, the pores on the head become clogged, the hairs become thin, and stop eating normally.
- Smoking and alcohol abuse. Smoking and drinking alcohol constricts blood vessels and clogs capillaries, as a result of which blood circulation is impaired not only in the hair growth zones, but throughout the human body.
Hair loss symptoms
Hair loss can be physiological or pathological. Physiological hair loss is associated with the hair cycle: in this case, 60 to 100 hairs fall out per day, and this is considered the norm.
There are situations when the biological balance is normal, that is, no more than 100 hairs are lost per day, but this happens all at once, so it seems that the hair has begun to “crawl in tufts”.
This usually happens in the following cases:
- If your hair has been in a tight hairstyle all day.
- If there was a long interval between shampooing or brushing.
- Sometimes the number of hair loss is much less than 100, but the overall appearance of the hair deteriorates and thinning is observed. This is possible in the following cases:
- In place of the lost hair, new ones do not grow.
- The hair itself becomes thinner.
Pathological hair loss can occur in different ways depending on the disease. Sometimes the hair condition worsens gradually, and the person does not immediately notice the problem. In this case, you can pay attention to some characteristic signs.
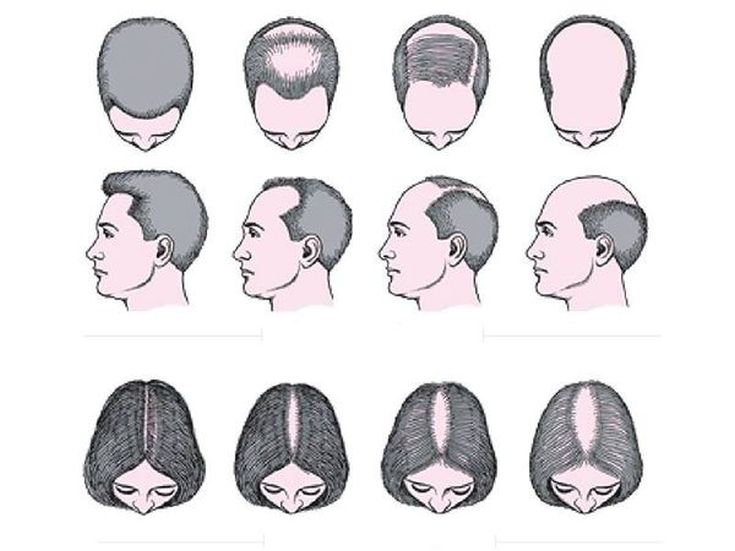
Features of hair loss in men:
- The hairline gradually rises higher, moving away from the eyebrows and temples.
- Gradually, the hair becomes thinner and lighter, their number is reduced, visually this is manifested by areas of thinning.
- Without correction, thinning becomes more pronounced and noticeable. Such negative dynamics is observed not over the entire surface of the head, but only in certain areas, while in other areas the hair grows in the same volume and quality.
In women, the process, as a rule, has its own characteristic features:
- Unlike men, hair thinning begins in the parting area. Sometimes it can take on the characteristic look of a “Christmas tree”: thinning and thinning of the hair is more pronounced in the central part, closer to the forehead, then the thinning area narrows along the parting, acquiring a triangular shape.
- Without correction, the negative dynamics intensifies, the hair becomes thinner and thinner, it is more difficult for patients to grow the length.
- Gradually the parting expands, the scalp is clearly visible through the hair, the hair does not grow back.
Another variant of the development of the process, when the hair begins to fall out very abruptly and abundantly. In this case the symptoms will be as follows:
- A large amount of hair remains on the comb, on bed linen, towels, in the bathroom drain and on household items.
- Areas of thinning or missing hair appear.
- Rashes and redness appear on the scalp.
- Patients can independently check whether the prolapse is pathological.
This requires:
- Remember what happened a few months ago. Was there serious stress, fever, whether the patient was taking any medications or dietary supplements.
- Analyze how long ago active loss began. Does this period exceed 3-4 months.
- Take a small lock of hair (about 50-100 hairs) in the area of the temples, pass it between your fingers and pull it slightly to the side. Then do the same with the strand in the crown area. If after such a test more than 5-7 hairs remain in the hands, then the problem exists.
- Collect hair and pay attention to the condition of the temporal zones (especially important for men, as well as for women in menopause). If bitemporal bald patches are observed (on the temples), then most likely there is a problem.
- For men. Compare the density of hair on different areas of the head. If there are areas where there is much less hair, then the condition is considered pathological.
- For women. Divide the hair on the head into two parts and evaluate the resulting parting. If it expands strongly as it approaches the forehead, then most likely the problem exists.
Classification and developmental stages of hair loss
There is no single, universal classification of hair diseases. However, they can be conditionally divided into two groups: cicatricial and non-cicatricial alopecia.
1. Cicatricial alopecia occur in 20% of cases. With alopecia of this group, tissue nutrition is disturbed and follicles atrophy, therefore, hair loss is irreversible. In order to have time to stop the pathological process, it is important to diagnose it as early as possible.
This group includes the following diseases:
- Brock's pseudo-pelada. The disease is characterized by the appearance of small areas of baldness in the parietal and frontal zones. There is redness of the skin in the affected areas, and the mouths of the hair follicles are absent. In the central part of the lesion, 1-2 long, unchanged hairs can be located. The course is long, while the hair is lost irretrievably.
- Hoffmann's abscessed, disruptive folliculitis. The occurrence of numerous abscesses, varying in size, is characteristic. After their resolution, cicatricial atrophy is observed in the areas of scalp inflammation. Hair growth in such areas does not resume.
- Lupus erythematosus. It is characterized by the appearance of areas of alopecia on the scalp in the form of discs with atrophy in the center. Usually, hair loss with lupus erythematosus is combined with a typical clinical picture of the disease. Specific skin lesions include a red rash primarily on the cheeks, nose, and chin. The presence of antibodies to DNA and antinuclear antibodies confirm the diagnosis.
- Scleroderma of the "blow with a saber" characterized by the appearance of a focus of sclerosis in the form of an ivory strip, resembling a scar. As a rule, it is located in the frontal zone of the scalp. The etiology of the disease remains poorly understood.
- Follicular mucinosis. This is a skin disease in which the structure of hair follicles and sebaceous glands is destroyed as a result of the deposition of mucin - the secretion of the body's mucous glands. It manifests itself as follicular papules and dense plaques, leading to hair loss.
- Physical damage to the scalp leaving scars.
2. Non-scarring alopecia occur in 80% of cases. They differ in that the prolapse proceeds without prior damage to the skin, and the follicles do not atrophy. This means that it is theoretically possible to restore growth at the site of the lost hair.
This group includes:
- Diffuse alopecia. It is the most common reason for contacting trichologists. With this type of alopecia, there is more hair loss than normal and the growth phase is shorter. Clinically, this is manifested by a sharp, profuse hair loss evenly from all areas of the scalp. The most common causes of diffuse alopecia are: neuropsychic stress; conditions accompanied by an increase in body temperature above 38.5 ° C; taking certain medications (NSAIDs, fibrates, antiestrogen drugs, antiviral drugs, immunomodulators, antidepressants).
- Androgenetic alopecia. It is characterized by thinning and thinning of hair in areas with an increased number of androgen receptors: in men - the parietal and frontal regions, in women - the area of the central parting of the head with distribution to the lateral surfaces. The reasons for the development of this type of alopecia are laid down at the genetic level and consist in the negative effect of dihydrotestosterone on the hair follicles.
- Nested (focal) alopecia. It is characterized by the appearance of smooth, hairless areas on the scalp. The areas can be single and multiple, total alopecia can develop with the loss of all hair on the scalp and on the body. The lifetime risk of alopecia areata is 1.7%, with the prevalence of pathology being 0.1%. This type of alopecia is often associated with autoimmune conditions such as vitiligo, thyroid disease, rheumatoid arthritis, and discoid lupus erythematosus. Sometimes the disease is accompanied by damage to the nail plates (point onychodystrophy).
- Hair loss for various diseases: secondary syphilis, leprosy (leprosy), fungal diseases, anemia, hypothyroidism, myxedema, etc.
Hair Loss Treatment
The choice of tactics for treating hair loss depends on the type and activity of the process. There are temporary factors, after the cessation of their effect, hair growth resumes in the same volume. Other factors require correction and treatment, and the earlier therapy is started, the fewer hair follicles will be involved in the pathological process.
Drug treatment
To treat hair problems, use:
- Inhibitors of androgenic metabolism Are first-line drugs for the treatment of androgenetic alopecia.
- Growth factor stimulants. The only substance from this group that is successfully used to correct androgenetic alopecia is minoxidil. To achieve a visible effect, you must use the drug for at least 9 months. But after canceling, the hair begins to fall out again.
- Hormonal and non-hormonal antiandrogenic drugs.
- Glucocorticosteroids. They are successfully used to treat alopecia areata.
- Antimetabolites and immunosuppressants for the treatment of common forms of alopecia areata.
- In special cases, may apply biological products, such as Janus kinase inhibitors.
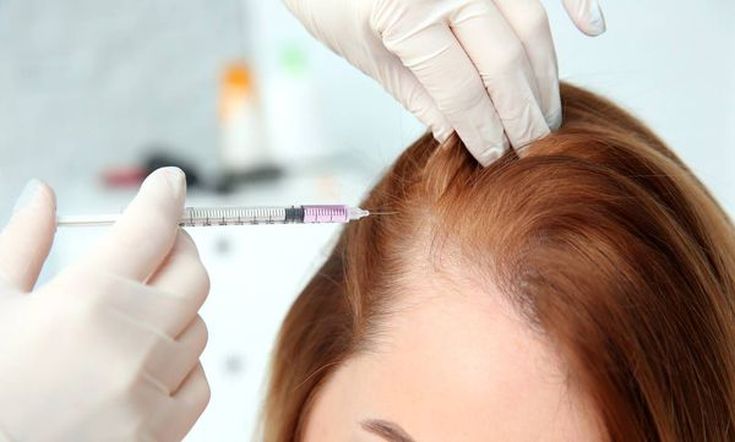
- PRP (plated rich plasma) - platelet-rich plasma. The technique consists in using platelet-rich blood plasma. For this, the patient's blood is placed in a special test tube and centrifuged. As a result, a layer rich in platelets and growth factors is detached, which stimulate tissue repair in the body. The resulting solution is injected intradermally or subcutaneously.
- Mesotherapy. The method is based on the introduction of various drugs intradermally. Efficiency is based on a combination of reflexogenic action from the injections themselves and the pharmacological action of the drug.
Surgery
In addition to therapeutic methods, surgical methods are also used - autotransplantation of hair follicles from areas where the growth and quality of hair is not disturbed. The disadvantage of the method is the non-guaranteed survival rate of follicles in new areas.
Physiotherapy treatment
Physiotherapy methods are used in the complex therapy of alopecia. These include: cryomassage, darsonvalization, PUVA therapy, galvanization, electrophoresis, light therapy. However, there is not enough reliable scientific data to prove the effectiveness of these techniques.
Conclusion
Thanks to the methods of modern medicine, the problem of hair loss is being successfully solved. The main thing is not to delay contacting a specialist who will conduct the necessary research and choose an effective method for solving your problem.